|
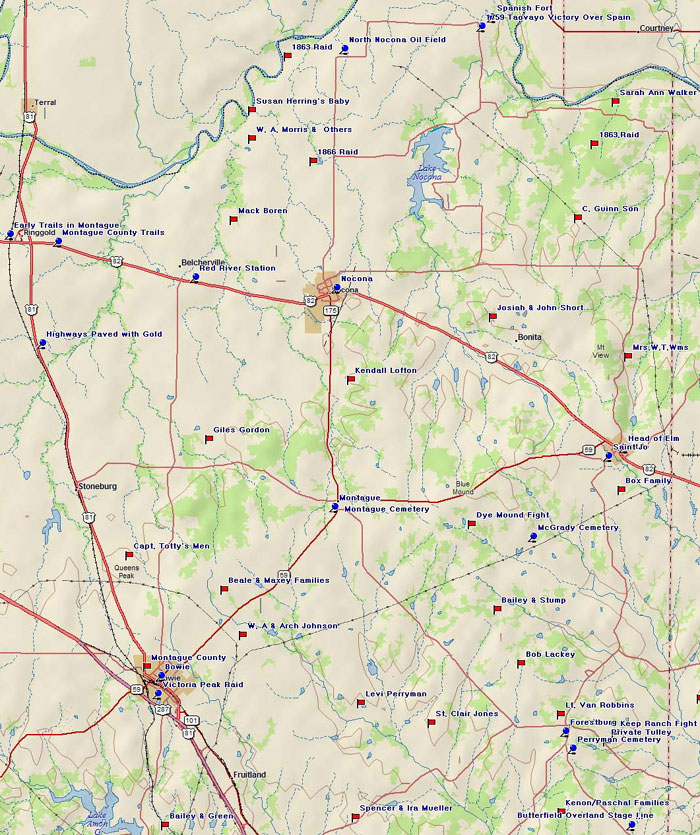
Marker Title: Brushy Mound
Address: Not located
City: Bowie
Marker Location: Not located, on private property.
Marker Text: From this lookout on whose summit an Indian chief lies
buried, Kiowas and Comanches spied on early settlers before launching
unexpected attacks.
Marker Title: Butterfield Overland Stage Line Crossing
Address: FM 455, about 5 mi. S of Forestburg
City: Forestburg
Year Marker Erected: 1936
Marker Location: From Forestburg take FM 455 about 5 miles south.
Marker Text: This is the crossing used by the Southern Overland Mail
Line connecting St. Louis and San Francisco with semi-weekly stage and
mail service 1858-1861; The length of the route, 2795 miles, and the
superior service maintained made this a pioneer enterprise of first
magnitude.
Marker Title: Forestburg
Address: SH 455, S of Forestburg
City: Forestburg
Year Marker Erected: 1936
Marker Location: On SH 455, south side of Forestburg.
Marker Text: Established after the Civil War in memory of its pioneers
who battled with the Indians, endured hardships and conquered the soil
that civilization might live.
Marker Title: Head of Elm (Saint Jo)
Address: US 82, (south side of square)
City: Saint Jo
Year Marker Erected: 1964
Marker Location: On US 82 (south side of square) in Saint Jo.
Marker Text: 1849-Capt. Randolph B. Marcy U.S. Government Survey Trip;
1854-Capt. John Pope Surveying proposed Federal Railroad; 1855-U.S.
2nd Cavalry Under Col. Albert Sidney Johnson en route to establish Texas
Frontier forts, reported settlement here; 1857-Col. James B. Llach Heading
"corn train" to Fort Belknap; 1860-First U.S. Post Office
John W. Womble Post Master; 1873-Saint Jo Founded On site by Capt. I.H.
Boggess & I.A. Bowell. (1964)
Marker Title: Highways Paved With Gold
Address: US 81, 5 mi. S of Ringgold
City: Ringgold
Year Marker Erected: 1963
Marker Location: From Ringgold take US 81 5 miles south to roadside
park.
Marker Text: From the immemorial man has searched for a land where streets
were paved with gold. As early as the 16th Century he was in Texas,
lured by Indian reports of "Seven Cities of Gold." They never
were found. But they provided the basis for legends of untold riches--stories
still spun by some Texans. Surprisingly, perhaps, many of the "tall
tales" are more fact than fiction. For instance, both this section
of U.S. Highway 81 and a portion of adjacent U.S. Highway 287 are actually
paved with gold! The story began in 1936 when the Texas Highway Department
was paving the two highways here in Montague County. Sand for the concrete
was taken from a nearby pit, opened three years earlier. The grains
glistened with such intensity as they were mixed that a closer examination
seemed prudent. So a small supply was sent to a Fort Worth laboratory
for assay. Back came the report: the sand contained gold. The news sent
the owner of the pit in feverish search of the mother lode. But in vain.
Top assays on his extensive "soundings" came to no more than
54 cents per ton of ore. His ardor was cooled further when he learned
the gold was not free but deeply imbedded in the sand. Disheartened,
he settled back into routine sand production. From his pit, however,
eventually came $250,000 in gold--all part of the sand. It has been
reckoned that as much as $31,000 is distributed along 39 miles of roadway.
Some $25,000 in U.S. Highway 81 and $6,000 in U.S. Highway 287. The
remainder has gone into other construction in the region, including
numerous buildings in which concrete has been used. So it is that today's
motorist has discovered the highways paved with gold and the "golden"
cities which his predecessors sought in vain. (1963)
Marker Title: McGrady Cemetery
Address: CR 401 off FM 3206, 4 mi. from Saint Jo
City: Saint Jo
Year Marker Erected: 1991
Marker Location: From Saint Jo take FM 3206 about 4 miles; head south
on County Road 401 to cemetery.
Marker Text: Allen R. McGrady and his wife Elizabeth (Cox) moved to
this area in 1859. They settled on 160 acres of land along Clear Creek.
This cemetery began in the 1860s after a McGrady employee was killed
by indians and buried on the family farm. One acre of land was set aside
for the graveyard, which became the final resting place for many McGrady
family members and neighbors. Allen and Elizabeth McGrady, both of whom
died in September 1899, are interred here. The cemetery stands as a
reminder of Montague County's pioneer heritage. (1991)
Marker Title: Montague Cemetery
Address: SH 175, N side of Montague
City: Montague
Year Marker Erected: 1985
Marker Location: One block east of SH 175, north side of town, Montague.
Marker Text: The first known settlers in Montague County arrived in
1849. After the county was formed in 1857, the City of Montague was
created a year later to serve as county seat. The town grew slowly at
first, but by 1871 was developing rapidly and experiencing an influx
of new settlers. James M. Gibbons, one of the early pioneers, came to
this area from Tennessee. Family history indicates that Gibbons donated
the first plot of land in this cemetery for the burial of his wife,
Elizabeth Lankford Gibbons, upon her death in 1862. He later married
Nancy Elizabeth Furr, who also is buried here. Gibbons died in 1899
and is interred in the cemetery, as are several other family members
and numerous other early settlers. The Montague Cemetery contains both
unmarked and marked graves. About 60 of the legible tombstones bear
dates from the 1800s. Several Confederate veterans and a few early Texas
Rangers also are buried here. With ties to the early settlement of Montague,
this graveyard is an important part of the area's history. Care for
the burial sites is provided by the Montague Cemetery Association. (1985)

Lt. Colonel Daniel Montague
Marker Title: Montague County
Address: US 81 on west side of Bowie
City: Bowie
Year Marker Erected: 1936
Marker Location: US 81, in city park (Meyers Park) on west side of Bowie.
Marker Text: Created December 24, 1857; organized August 2, 1858; named
in honor of Daniel Montague 1798-1876; Pioneer Texas surveyor and Indian
fighter; commander of a company in the Mexican War; Montague, County
Seat
Marker Title: Montague County Trails
Address: US 82, east side of Nocona
City: Nocona
Year Marker Erected: 1986
Marker Location: On US 82, east side of Nocona.
Marker Title: Early Trails in Montague County
Address: US 82, 1 mi west of Ringgold
City: Ringgold
Year Marker Erected: 1969
Marker Location: From Ringgold take US 82 1 mile west.
Marker Text: Lying on a direct line of travel from the United States
to Mexico, California, and points west, the area now Montague County
was once a network of trails. One of the first area roads forged by
white men was the Chihuahua Traders Trail of 1840. Blazed by merchants
hoping to open a trade route from Mexico to St. Louis, Mo., this road
crossed present Montague County and left tracks for later travelers.
In 1841 came the Texan-Santa Fe Expedition; though it failed to open
regular commerce between the Republic of Texas and Northern Mexico,
this delegation also left a road and enforced the claims of Texas to
Western territories. In 1849 U.S. Army Capt. Randolph B. Marcy charted
a "California Trail", using parts of older routes. This soon
grew into a thoroughfare for forty-niners and sturdy pioneers who came
later. In 1858 the famous Butterfield Overland Mail Line came across
the county; and in the 1870's, as Texas was building her image as a
cattle empire, Montague County was crossed by two feeder branches of
the Chisholm Trail. In 1882, the county's first railroad followed much
of the Texan-Santa Fe Trail. Today Highway 82 partly traces Marcy's
route and other roads parallel many of these early trails. (1969)
Marker Title: Montague Pioneer Memorial
Address: Courthouse square
City: Montague
Year Marker Erected: 1958
Marker Location: Northwest corner county courthouse square, Montague.
Marker Title: North Nocona Oil Field - Montague County Oil Discovery
1922
Address: FM 103, 10 mi. W of Nocona
City: Nocona
Year Marker Erected: 1972
Marker Location: From Nocona take FM 103 about 10 miles north.
Marker Text: Pennsylvania oil man George Williams, backed by Cad McCall,
drilled for oil intermittently, 1918-22, beginning at Eagle Point (4.5
mi. SE). Leasing by individuals and major companies--including Phil
Lesh, A.E. Humphrey, and the Texas Co.--kept rigs working. Gas blew
in at 800-foot depth on J.W. Maddox-J.E. Lemons land, one well yielding
over 100,000,000 cubic feet daily. The gas was piped to Nocona and rural
homes. Oil was discovered in 1922 on Maddox site, at about 1,000 feet.
Production continued at 1,000-2,000 feet, there and elsewhere. The gas
caused trouble: a capped well blew mud from prairie dog holes and gas
from water well a quarter-mile away. In 1925, a gas well on W.W. Jones
land (2 mi. W) blew out a gigantic crater. Another well (.75 mi. W)
caught fire, burned its rig, and was finally doused by nationally-famed
oil well fire fighter Tex Thornton. With an estimated 100,000,000-barrel
total on record, this 12,295-acre field still produces. (1972)
Marker Title: Perryman Cemetery
Address: FM 455, NW of Forestburg
City: Forestburg
Year Marker Erected: 1983
Marker Location: From Forestburg take FM 455 about one mile to cemetery.
Marker Text: The first marked grave in this burial ground is than of
an infant who died in 1862. Other burials include those of a Mr. Jones,
a well-digger killed by Indians in 1863, and Dory Booher and Ben Steadham,
former Confederate soldiers who had been captured at Lookout Mountain,
Tenn. during the Civil War. In 1883 the cemetery was purchased by Levi
Perryman (1839-1921) and deeded to Montague County. A Forestburg community
leader, Perryman had been a Confederate soldier, an indian fighter,
and sheriff. Still used, this cemetery serves as a reminder of the area's
pioneers. (1983)
Marker Title: Queen's Peak Indian Lookout
Address: Not Located
City: Bowie
Marker Location: Not Located - on private property.
Marker Text: Discovered by white men in 1848. Permanent white settlement
began in this region in 1858. Its early history is a long story of Indian
raids. In memory of pioneer women, who, in the midst of such dangers,
daily risked their lives for others, this monument is erected.
Marker Title: Red River Station
Address: Not Located
City: Bowie
Marker Location: Not located - private property.
Marker Text: "Jumping-off point" on the famous Chisholm Cattle
Trail, (1867-87), Red River Station was a main crossing and last place
on trail to buy supplies until Abilene, Kan.--350 miles north. During
the cattle drive era of Western history, millions of animals swam the
turbulent river here en route to Kansas railhead and markets. An abrupt
bend in the river checked its flow at this point, creating a natural
crossing which had been used for years by buffalo and Indians. Even
so, the water was wide, swift, and sometimes clogged with sand bars.
Frequently cattle were so jammed cowboys could walk across on their
backs. Besides a cattle crossing, the station was an outpost of the
frontier regiment, which patrolled Texas' northernmost border during
Confederacy (1861-65). During cattle era, a town began here, its ferry
serving drovers, soldiers, freighters, and settlers returning from Indian
captivity. Local cemetery (1 mi. SE) contains many graves of these Texas
pioneers. (1971)
Marker Title: Red River Station
Address: US 82, 6 mi. W of Nocona
City: Nocona
Year Marker Erected: 1963
Marker Location: On US 82 6 miles west of Nocona.
Marker Text: Established 9 miles northwest 1861 as Civil War outpost
near major buffalo and Indian crossing. Local soldiers, determined to
guard edge of settlement against Indian raids, Union invasion from Indian
territory, joined by Texas Frontier Regiment Cavalry Company. Families
of settlers, cattlemen built log cabins within post stockade. Poorly
fed, clothed and short on horses and ammunition Confederates patrolled
area effectively. Comanche, Kiowa raid at Illinois Bend 15 miles east
Jan. 1863. Major cattle crossing after war. A memorial to Texans who
served in the Confederacy - Erected by the State of Texas 1963; (BACK
OF RED RIVER STATION) Texas Civil War Frontier Defense 1861-1865 Texas
made an all-out effort for the Confederacy after voting over 3 to 1
for secession. 90,000 troops, noted for mobility and and heroic daring,
fought on every battlefront. An important source of supply and gateway
to foreign trade thru Mexico, Texas was the storehouse of the south.
Red River Station and other posts on this line were backed by patrols
of state Rangers, organized militia, and citizens posses scouting from
nearby "family forts." This was part of a 2000 mile frontier
and coastline successfully defended by Texans. (1963) More
Marker Title: Town of Saint Jo
Address: FM 677, in city park
City: Saint Jo
Year Marker Erected: 1972
Marker Location: FM 677 at city park, Saint Jo.
Marker Text: One of oldest towns in Montague County. Founded in 1850s,
during great California Gold Rush, by E.S. and Ithane Singletary (Brothers)
and John Hughes, who hoped to find gold here. The community they started
became known as "Head of Elm" for its location at headwaters
of Elm Fork of Trinity River. In 1858 Head of Elm ran--and lost--race
for county seat. A post office opened here (at site of marker) in 1859,
with John Womble, another pioneer, as postmaster. An early store and
saloon were owned by Dominick Burns. Next spurt of growth for town came
with locating of Chisholm Cattle Trail through here about 1868. In 1871
village had a post office, blacksmith shop, and five stores. In 1872
I.H. Boggess (owner of the famous Stonewall Saloon) and Joe Howell bought
640 acres of land and laid out townsite, which Boggess named "Joe",
for Howell. One story says he decided to add "Saint" because
Joe was a staunch non-drinker; another version claims he added it to
make the name longer. In 1874 citizens built an all-faiths church and
in 1876 a newspaper was established. Saint Jo was organized as a town
in 1880; incorporated in 1886. Population has remained about 1,000 since
that time and economy is still based on farming and ranching. (1972)
Marker Title: Spanish Fort
Address: FM 103, 17 mi. W of Nocona
City: Spanish Fort
Year Marker Erected: 1936
Marker Location: From Nocona take FM 103 about 17 miles to Spanish fort.
Marker is on square across from old store.
Marker Text: The Commission allocated $1,500 for the monument erected
near the site of the original fort. The shaft of Texas red granite rises
eight feet above its triple-stepped base. The plaque, designed by Raoul
Josset, symbolizes the Taovayas Indian and relates the early history
of the region. The memorial was designed by Page & Southerland,
architects. The town of Spanish Fort. Occupies the Site of an Ancient
Taovayas Indian Village. Scene of first severe defeat in Texas of Spanish
troops by Indians in 1859. Named Fort Teodoro in 1778 by De Mezieres
in honor of Teodoro De Croix, Commander of the Interior Provinces of
Mexico. Permanent white settlements began in this vicinity after 1850.
"Let the grandeur of the pioneer be discerned in the safety he
has secured, in the good he has accomplished, in the civilization he
has established." (1936)
Marker Title: Site of the 1759 Taovayo Victory Over Spain
Address: FM 103, town square
City: Saint Jo
Year Marker Erected: 1976
Marker Location: From Nocona take FM 103 about 17 miles to Spanish Fort
Marker is located next to large granite monument in center of town.
Marker Text: Col. Diego Ortiz Parilla, a commandant of Presidio San
Saba (near the later site of Menard) had grave Indian problems in 1759.
Priests and others were killed in Comanche attacks on Mission San Saba.
Comanches and their friends were allied to Frenchmen, who were trading
deep in Spanish domain. Parilla wished to whip the Comanches and expel
the French. With 380 soldiers and Indian support to a total of 600 men,
he left San Antonio in August. A victory over some Tonkawas on the Brazos
as he marched north gave him false confidence. When he arrived at this
site in October, he saw Red River forming a moat around a fort. His
Apaches tried in vain to span the river and invade the fortified Taovaya
village. He saw 14 or more Frenchmen; a French flag was flying. Indians
played drum and fife and had plenty of guns and ammunition. He bombarded
the fort with cannons, but after losing 52 men in a 4-hour battle he
was glad that nightfall gave him a chance to withdraw. He was pursued
for many days as he retreated to Presidio San Saba, which he reached
on Oct. 25, 1759. The Taovaya Indians were later known as Wichitas,
and continued to resist white men until the 1870s. (1976) |